How to Install and Configure OpenVAS on Ubuntu 20.04

I’ve worked with a few vulnerability scanners over the years, and OpenVAS has always stood out for one reason it just works. It’s open-source, runs on Linux, and digs through your servers looking for the weak spots you probably don’t want to find the hard way.
It started out as Open Vulnerability Assessment System and, somewhere along the way, grew into Greenbone Vulnerability Management (GVM) the same engine underneath, but with a lot more polish and regular updates. In this walkthrough, I’ll show you how to get OpenVAS running on Ubuntu 20.04. Nothing fancy just the steps you actually need to end up with a working scanner.
If you don’t have a test server handy, you can spin up a quick Ubuntu VPS from Eldernode it’s stable, clean, and perfect for experimenting.
To let this tutorial work better, please consider the below Prerequisites:
– A non-root user with Sudo privileges.
– To set up, follow our Initial server setup on Ubuntu 20.04.
– At least 4 GB RAM.
– At least 4 vCPUs.
– More than 8 GB disk space.
Install GVM (OpenVAS) on Ubuntu 20.04
Let’s go through the steps of this guide and be an expert in OpenVAS installation. As always, start with updating your system packages. Use the command below to update your system packages to the latest version:
apt-get update -y
How to install Prerequisites
First of all, you need to install the following dependencies packages.
sudo su -
apt update &&\
apt -y dist-upgrade &&\
apt -y autoremove &&\
apt install -y software-properties-common &&\
apt install -y build-essential cmake pkg-config libglib2.0-dev libgpgme-dev libgnutls28-dev uuid-dev libssh-gcrypt-dev libldap2-dev doxygen graphviz libradcli-dev libhiredis-dev libpcap-dev bison libksba-dev libsnmp-dev gcc-mingw-w64 heimdal-dev libpopt-dev xmltoman redis-server xsltproc libical-dev postgresql postgresql-contrib postgresql-server-dev-all gnutls-bin nmap rpm nsis curl wget fakeroot gnupg sshpass socat snmp smbclient libmicrohttpd-dev libxml2-dev python3-polib gettext rsync xml-twig-tools python3-paramiko python3-lxml python3-defusedxml python3-pip python3-psutil python3-impacket virtualenv vim git &&\
apt install -y texlive-latex-extra --no-install-recommends &&\
apt install -y texlive-fonts-recommended &&\
curl -sS https://dl.yarnpkg.com/debian/pubkey.gpg | apt-key add - &&\
echo "deb https://dl.yarnpkg.com/debian/ stable main" | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/yarn.list &&\
apt update &&\
apt -y install yarn &&\
yarn install &&\
yarn upgrade
How to create the GVM user
Now, you must create the GVM user. Open the terminal and paste the commands below to create the GVM user. Then, it will be used in the installation and compilation process.
echo 'export PATH="$PATH:/opt/gvm/bin:/opt/gvm/sbin:/opt/gvm/.local/bin"' | tee -a /etc/profile.d/gvm.sh &&\
chmod 0755 /etc/profile.d/gvm.sh &&\
source /etc/profile.d/gvm.sh &&\
bash -c 'cat < /etc/ld.so.conf.d/gvm.conf
# gmv libs location
/opt/gvm/lib
EOF'
mkdir /opt/gvm &&\
adduser gvm --disabled-password --home /opt/gvm/ --no-create-home --gecos '' &&\
usermod -aG redis gvm &&\
chown gvm:gvm /opt/gvm/
Now, you can log in to GVM user:
sudo su - gvm
How to download and install GVM
In this step, you will download and install software by creating the src folder and git clone the GVM source code. So, navigate to the temporary directory created above and run the subsequent commands.
mkdir src &&\
cd src &&\
export PKG_CONFIG_PATH=/opt/gvm/lib/pkgconfig:$PKG_CONFIG_PATH
git clone -b gvm-libs-20.08 --single-branch https://github.com/greenbone/gvm-libs.git &&\
git clone -b openvas-20.08 --single-branch https://github.com/greenbone/openvas.git &&\
git clone -b gvmd-20.08 --single-branch https://github.com/greenbone/gvmd.git &&\
git clone -b master --single-branch https://github.com/greenbone/openvas-smb.git &&\
git clone -b gsa-20.08 --single-branch https://github.com/greenbone/gsa.git &&\
git clone -b ospd-openvas-20.08 --single-branch https://github.com/greenbone/ospd-openvas.git &&\
git clone -b ospd-20.08 --single-branch https://github.com/greenbone/ospd.git
How to install gvm-libs
It is time to install and compile the gvm-libs from GitHub. Use the commands below to change the directory to gvm-libs, export the config path and create a build directory.
cd gvm-libs &&\
export PKG_CONFIG_PATH=/opt/gvm/lib/pkgconfig:$PKG_CONFIG_PATH &&\
mkdir build &&\
cd build &&\
cmake -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/opt/gvm .. &&\
make &&\
make doc &&\
make install &&\
cd /opt/gvm/src
How to install openvas-smb
Use the commands below to enter the Openvas-smb directory and compile the source code.
cd openvas-smb &&\
export PKG_CONFIG_PATH=/opt/gvm/lib/pkgconfig:$PKG_CONFIG_PATH &&\
mkdir build &&\
cd build/ &&\
cmake -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/opt/gvm .. &&\
make &&\
make install &&\
cd /opt/gvm/src
How to install OpenVAS Scanner
again, you need to build and install the OpenVas scanner.
cd openvas &&\
export PKG_CONFIG_PATH=/opt/gvm/lib/pkgconfig:$PKG_CONFIG_PATH &&\
mkdir build &&\
cd build/ &&\
cmake -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/opt/gvm .. &&\
make &&\
make doc &&\
make install &&\
cd /opt/gvm/src
How to fix Redis for OpenVAS install
To log out of the current session to get back to the privileged user, you should type ‘exit’ in the terminal. Then, paste the following code.
export LC_ALL="C" &&\
ldconfig &&\
cp /etc/redis/redis.conf /etc/redis/redis.orig &&\
cp /opt/gvm/src/openvas/config/redis-openvas.conf /etc/redis/ &&\
chown redis:redis /etc/redis/redis-openvas.conf &&\
echo "db_address = /run/redis-openvas/redis.sock" > /opt/gvm/etc/openvas/openvas.conf &&\
systemctl enable [email protected] &&\
systemctl start [email protected]
sysctl -w net.core.somaxconn=1024 &&\
sysctl vm.overcommit_memory=1 &&\
echo "net.core.somaxconn=1024" >> /etc/sysctl.conf &&\
echo "vm.overcommit_memory=1" >> /etc/sysctl.conf
systemctl daemon-reload &&\
systemctl start disable-thp &&\
systemctl enable disable-thp &&\
systemctl restart redis-server
At this point, you should add /opt/gvm/sbin path to the secure_path variable:
sed 's/Defaults\s.*secure_path=\"\/usr\/local\/sbin:\/usr\/local\/bin:\/usr\/sbin:\/usr\/bin:\/sbin:\/bin:\/snap\/bin\"/Defaults secure_path=\"\/usr\/local\/sbin:\/usr\/local\/bin:\/usr\/sbin:\/usr\/bin:\/sbin:\/bin:\/snap\/bin:\/opt\/gvm\/sbin\"/g' /etc/sudoers | EDITOR='tee' visudo
Now, use the following commands to allow the user running ospd-openvas to launch with root permissions.
echo "gvm ALL = NOPASSWD: /opt/gvm/sbin/openvas" > /etc/sudoers.d/gvm
echo "gvm ALL = NOPASSWD: /opt/gvm/sbin/gsad" >> /etc/sudoers.d/gvm
How to update NVT
In this section, you will update vulnerability file definitions. To do this the greenbone-nvt should be run. But first, switch back to the GVM user session.
sudo su – gvm
And then, type:
greenbone-nvt-sync
You may face timeout errors because of a firewall. Open TCP port 873 and if you get connection refused errors, go for a coffee and back again. It will take a very long time.
Upload plugins in Redis with GVM
Uploading plugins in Redis with OpenVAS will be time-consuming depending on your hardware. Also, you will receive no feedback when you run the command.
sudo openvas -u
Run the following if you get missing library errors.
exit
echo "/opt/gvm/lib > /etc/ld.so.conf.d/gvm.conf
ldconfig
sudo su - gvm
Install GreenboneManager
To build and install Greenbone Manager, enter the gvmd directory:
cd /opt/gvm/src/gvmd &&\
export PKG_CONFIG_PATH=/opt/gvm/lib/pkgconfig:$PKG_CONFIG_PATH &&\
mkdir build &&\
cd build/ &&\
cmake -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/opt/gvm .. &&\
make &&\
make doc &&\
make install &&\
cd /opt/gvm/src
How to configure PostgreSQL
To configure PostgreSQL, switch to a user in sudoers. The user session will be switched with the “sudo -u postgres bash” command below.
Note: Do not use root or gvm and execute one line at a time.
exit
cd /
sudo -u postgres bas
export LC_ALL="C"
createuser -DRS gvm
createdb -O gvm gvmd
psql gvmd
create role dba with superuser noinherit;
grant dba to gvm;
create extension "uuid-ossp";
create extension "pgcrypto";
exit
exit
How to fix Certificates
To fix GVM certificates, type one line at the time:
sudo su - gvm
gvm-manage-certs -a
How to create an Admin user
Run the below command to create an initial username and password but do not forget to change it.
gvmd --create-user=admin --password=admin
How to configure and update feeds
Set ”Feed Import Owner” to the admin’s UUID. It lets the feeds be updated completely. To find the UUID of the new admin user, type:
gvmd --get-users --verbose
There, you will get something as below:
admin fb019c52-75ec-4cb6-b176-5a55a9b360bf
And then, run:
gvmd --modify-setting 78eceaec-3385-11ea-b237-28d24461215b --value (output string from the above command fb019c52-75ec-4cb6-b176-5a55a9b360bf)
So the example command would be:
$ gvmd --get-users --verbose
admin fb019c52-75ec-4cb6-b176-5a55a9b360bf
$ gvmd --modify-setting 78eceaec-3385-11ea-b237-28d24461215b --value fb019c52-75ec-4cb6-b176-5a55a9b360bf
Next, run the following commands one line at a time. You may get connection refused errors but run again till it succeeds. Consider that these commands may take some time.
greenbone-feed-sync --type GVMD_DATA
greenbone-feed-sync --type SCAP
greenbone-feed-sync --type CERT
How to install GSA
To install GSA (GVM), enter the GSA folder and compile the GSA source code.
cd /opt/gvm/src/gsa &&\
export PKG_CONFIG_PATH=/opt/gvm/lib/pkgconfig:$PKG_CONFIG_PATH &&\
mkdir build &&\
cd build/ &&\
cmake -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/opt/gvm .. &&\
make &&\
make doc &&\
make install &&\
touch /opt/gvm/var/log/gvm/gsad.log &&\
cd /opt/gvm/src
Set up OSPD-OpenVAS and Install the virtualenv
cd /opt/gvm/src &&\
export PKG_CONFIG_PATH=/opt/gvm/lib/pkgconfig:$PKG_CONFIG_PATH &&\
virtualenv --python python3.8 /opt/gvm/bin/ospd-scanner/ &&\
source /opt/gvm/bin/ospd-scanner/bin/activate
Note: To match your installed python version, you may have to change _python python3.8
How to Install ospd
Use pip installer to install ospd as follows:
mkdir /opt/gvm/var/run/ospd/ &&\
cd ospd &&\
pip3 install . &&\
cd /opt/gvm/src
Install ospd-openvas
Again, use pip installer to install ospd-openvas.
cd ospd-openvas &&\
pip3 install . &&\
cd /opt/gvm/src
How to create startup scripts
To create startup scripts (root) paste the command below. Before that, you should type exit to log out to the root session.
cat << EOF > /etc/systemd/system/gvmd.service
[Unit]
Description=Open Vulnerability Assessment System Manager Daemon
Documentation=man:gvmd(8) https://www.greenbone.net
Wants=postgresql.service ospd-openvas.service
After=postgresql.service ospd-openvas.service
[Service]
Type=forking
User=gvm
Group=gvm
PIDFile=/opt/gvm/var/run/gvmd.pid
WorkingDirectory=/opt/gvm
ExecStart=/opt/gvm/sbin/gvmd --osp-vt-update=/opt/gvm/var/run/ospd.sock
ExecReload=/bin/kill -HUP $MAINPID
KillMode=mixed
Restart=on-failure
RestartSec=2min
KillMode=process
KillSignal=SIGINT
GuessMainPID=no
PrivateTmp=true
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOF
cat << EOF > /etc/systemd/system/gsad.service
[Unit]
Description=Greenbone Security Assistant (gsad)
Documentation=man:gsad(8) https://www.greenbone.net
After=network.target
Wants=gvmd.service
[Service]
Type=forking
PIDFile=/opt/gvm/var/run/gsad.pid
WorkingDirectory=/opt/gvm
ExecStart=/opt/gvm/sbin/gsad --drop-privileges=gvm
Restart=on-failure
RestartSec=2min
KillMode=process
KillSignal=SIGINT
GuessMainPID=no
PrivateTmp=true
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOF
How to enable and start the services
As root user, enable and start the GVM services:
systemctl daemon-reload &&\
systemctl enable gvmd &&\
systemctl enable gsad &&\
systemctl enable ospd-openvas &&\
systemctl start gvmd &&\
systemctl start gsad &&\
systemctl start ospd-openvas
How to check the services
Run the following command one in line at a time and make sure all three services are running.
systemctl status gvmd
systemctl status gsad
systemctl status ospd-openvas
How to modify default scanner
To modify the default scanner (GVM), switch back to your GVM session.
sudo su - gvm
To get the UUID of the scanner that has the socket (ospd.sock), run:
gvmd --get-scanners
Next, use the command below to modify the scanner.
gvmd --modify-scanner=(INSERT SCANNER UUID HERE) --scanner-host=/opt/gvm/var/run/ospd.sock
How to access the GVM web interface
You can access the GVM web interface using the URL https://your-server-ip since it is installed and listening on ports 80 and 443. So, you will be redirected to the GVM login page as you see below:
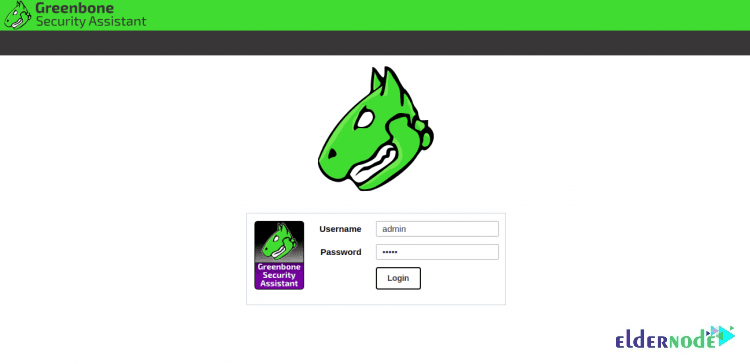
To log in to GVM, provide your admin username, password and click on the Login button. Then, you will see the GVM dashboard as follows:
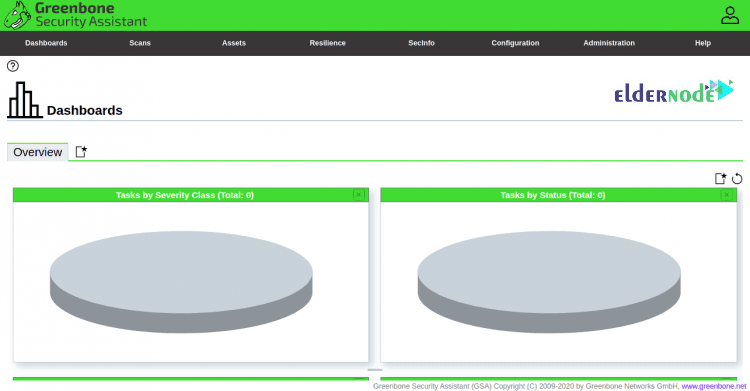
The default login is admin/admin as set above. The web interface of OpenVAS offers many operations in its Configuration tab. Explore the options, make necessary modifications, and run an advanced scan using different targets, scan configs, and credentials.
Using Advanced Scan Options in OpenVAS
If you wish to have a greater level of control over your scans, the Advanced Task Wizard has been designed for you. You can access it by browsing the path below:
Scans >> Tasks and clicking the purple button
The advanced wizard will offer you some scanning options such as: Setting a name for the task, choosing a scan config, setting the target IP address, scheduling future scans, and using a credentialed scan.
Several default scan configs are provided by OpenVAS that allow you to create custom configs. Browse to Configuration >> Scan Configs to see the descriptions of scan configs and create new ones. You can also see the details of each scan config if you click on them. Click on the blue star button in the top left corner, create the config, and then click in to edit it to be able to create a new scan.
Conclusion
So that’s pretty much it. If everything went right, OpenVAS should be up and running on your Ubuntu 20.04 box. Go ahead open the dashboard, run a small test scan, and see what kind of results you get. The first run usually tells you a lot about how things actually work.
After that, tweak a few settings, add your own targets, maybe break something and fix it again that’s honestly how most admins get comfortable with tools like this. And if you’re curious about trying the same setup on another distro, there’s also a CentOS 7 version of this guide on Eldernode.